HIGH-DOSE INTRAVENOUS VITAMIN C IN COMBINATION WITH 2-DEOXY GLUCOSE (2DG)
Intravenous Vitamin C in cancer
Vitamin C is being taken in dietary and supplementary forms. It has proved to be detrimental to cancer cells. It is given to cancer patients of different cancer types and harms only tumor cells without affecting the normal body cells. So, ascorbic acid or any of its derivatives can be a promising therapeutic strategy for cancer.
Vitamin C or ascorbic acid alters the glucose metabolism of the cancer cells. The most important hallmark of tumor cells is increased energy production by glycolysis, or the Warburg effect. They take up glucose from the environment and produce energy by glycolytic pathway instead of oxidative phosphorylation as done by normal body cells. Glucose binds the glucose transporters and is converted to pyruvate by glycolysis (Carr & Cook, 2018).
When vitamin C is administered in the cell, it will bind the glucose transporters and limit them to binding of glucose, thus cancer cells will not be able to take excess glucose, and not enough energy production takes place in the tumor cells. Tumor cells have increased proliferation and growth, so they need a large amount of energy for their survival. When enough energy will not be produced, cells will not be able to perform their basic survival functions and will ultimately die.
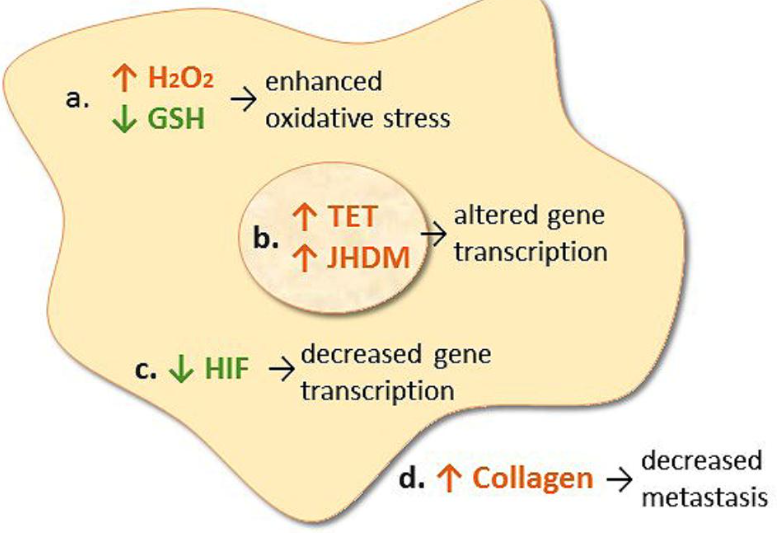
Moreover, vitamin C produces reactive oxygen species ROS in the tumor cells, which will cause oxidative stress, and this will also halt cell survival affecting many biochemical processes in the cells and killing them.
Vitamin C and many of its derivatives are being used in different anti-cancer studies. Many human and preclinical trials have been performed to check the correlation between vitamin C and cancers. And significant outcomes have been observed (Codini, 2020).
2DG and Cancer
2DG is an analog of glucose and an inhibitor of glycolysis. It is also being used as an important therapeutic strategy against cancer. It only targets cancer cells without any harm to the normal cells and has the ability to kill the cancer cells. It is also given after cancer treatment patients in order to prevent tumor recurrence later in life.
2DG has structural similarity with the glucose molecule. As cancer cells require a lot of glucose to meet their energy needs by glycolysis even in the presence of oxygen. Cancer cells will take up 2DG bound to the glucose transporters instead of a normal glucose molecule. It is converted to phosphor form by hexokinase enzyme, but it cannot be metabolized like the normal glucose molecule and hence, can not produce energy. When cancer cells become deprived of energy, they cannot perform metabolic activities and hence, cannot survive. So, 2DG is being used to kill tumor cells of any type.
Normal cells can produce energy by oxidative phosphorylation as well. So, if glucose cannot bind to glucose transporters, they will have another option for energy production and survival. So, these are not harmed by 2DG (Bonuccelli et al., 2017).
Intravenous Vitamin C in combination with 2DG
As mentioned above, vitamin C and 2DG both are being used against the tumor cells, and both have the ability to target the glucose or energy-producing metabolism of the cancer cells. So, many experiments have been performed in vivo and in vitro to check the combined effects of vitamin C injected intravenously and 2DG given to cancer patients. Significant results have been seen when these are used as a combination therapy against cancer.
In vitro Experiments
Experiments were performed on the breast cancer cell lines to check the combined effects of vitamin C and 2DG against tumor activity. Some cell lines were given 2DG alone, some were given Vitamin C alone, and the third group of cell lines was given both vitamin C and 2DG.
After a few weeks, tumor activity was observed in all the cell lines to check if the combined action is more effective than individual therapies or not. It was observed that the cell lines that were given both therapies simultaneously, i.e., vitamin C and 2DG showed more effective results, as tumor size was greatly reduced in these as compared to the cell lines receiving 2DG or vitamin C therapies individually. So, in vitro experiments proved that the combined action of 2DG and vitamin C is more effective for different cancer types.
In vivo Experiments
After passing the in vitro experiments, the same findings were done in vivo using animal models. Mice were used as model organisms and were divided into multiple groups. These were injected with a mutagen to make breast cancer models and later, one group was used as a control that was not given therapy. Another group was given 2DG alone to treat cancer, one more group was given vitamin C alone, while the last group was given both vitamin C and 2DG. Vitamin C was injected intravenously into the mice and standard doses were given on a daily basis. After a few weeks results were observed in all the mice groups.
The mice group that was given 2DG or Vitamin C therapies alone showed tumor reduction, but the group that was given both therapies in combination showed a greater reduction in the tumor as compared to both of these groups and the control. So, the combined action of 2DG and vitamin C proved to be more severe against the tumors as compared to their individual effects (De Francesco et al., 2017). Hence, this combination therapy can be more promising than conventional therapies in the near future.
Human Trials
Human trials are also being performed on cancer patients to check the effectiveness of the therapy. It is observed that the last stage cancer patients lack vitamin C in their bodies although it is an important component in many important pathways acting as a coenzyme and also stimulates the body’s immune system. So, giving vitamin C to these patients helps them fight against cancer.
Cancer patients were given 2DG in combination with vitamin C that was injected intravenously, and it was observed that the rate of tumor reduction increases in these patients significantly. Vitamin C induces apoptosis in the cancer cells. It also kills the tumor cells by increasing oxidative stress and by inhibiting HIF-1 which is very important for the survival of malignant cells under low oxygen conditions.
So, the combined use of 2DG and vitamin C will kill the tumor cells by acting through different mechanisms from targeting the sugar metabolism to inducing apoptosis. This combinational therapy can be used following the standard treatment conditions for treating almost all types of cancer patients (Satheesh et al., 2020).
Conclusion
2DG, a glucose analog, targets glucose metabolism in cancer cells. Vitamin C targets sugar metabolism as well as induces apoptosis in malignant cells. When both 2DG and vitamin C are used in combination, they have more significant outcomes in treating cancer. Both of these targets the tumor cells without affecting normal body cells present around them.
References
Bonuccelli, G., De Francesco, E. M., de Boer, R., Tanowitz, H. B., & Lisanti, M. P. (2017). NADH autofluorescence, a new metabolic biomarker for cancer stem cells: Identification of Vitamin C and CAPE as natural products targeting “stemness.” Oncotarget, 8(13), 20667–20678. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15400
Carr, A. C., & Cook, J. (2018). Intravenous vitamin C for cancer therapy – Identifying the current gaps in our knowledge. Frontiers in Physiology, 9(AUG). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01182
Codini, M. (2020). Why vitamin C could be an excellent complementary remedy to conventional therapies for breast cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(21), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218397
De Francesco, E. M., Bonuccelli, G., Maggiolini, M., Sotgia, F., & Lisanti, M. P. (2017). Vitamin C and Doxycycline: A synthetic lethal combination therapy targeting metabolic flexibility in cancer stem cells (CSCs). Oncotarget, 8(40), 67269–67286. https://doi.org/10.18632/ONCOTARGET.18428
Satheesh, N. J., Samuel, S. M., & Büsselberg, D. (2020). Combination therapy with vitamin C could eradicate cancer stem cells. Biomolecules, 10(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010079
