
Antisense oligonucleotide therapy plays a vital role in cancer and genetic disorders. This therapy involves the use of oligonucleotides that are complementary to specific target DNA or RNA in the nucleus. Oligonucleotides bind the complementary sequence and inhibit the synthesis of specific proteins by different mechanisms. Thus, downregulating the expression of target genes.

What are Oligonucleotides?
Oligo means “Few”. These are short double stranded RNA molecules which consist of sequences of AGCU nucleotides storing the genetic information.Types of Oligonucleotides
- miRNA
- siRNA, Primers (Natural) and
- Antisense Oligonucleotides
What are Oligonucleotides used for?
Oligonucleotides are used in treatments for gene defects and Metabolic disorders. Therapeutic Oligonucleotides target the mRNA and change gene expression (proteins).Antisense Oligonucleotides
These are Oligonucleotides which cuts the expression of proteins with in a cell.Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy (AOT)
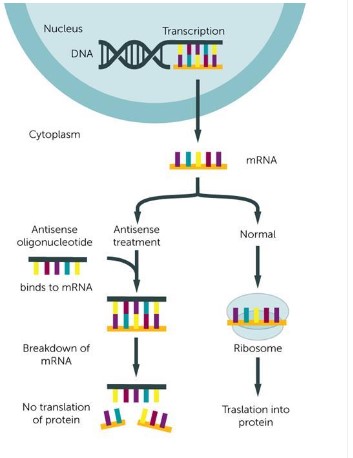
The use of oligonucleotides that are complementary to our target mRNA in order to reduce the expression of some specific gene in a cell is called antisense therapy. These oligonucleotides bind in the 5 to 3 directions with mRNA and do not allow it to translate into proteins. So, a low quantity of protein is formed, and loss of function occurs in the cell.
Many antisense therapeutic drugs are available in the market and are being used for the treatment of multiple disorders like cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and arthritis. All these drugs are approved by FDA.
The oligonucleotides that are available naturally are usually unstable or with low stability and efficacy as they have a lot of side effects. So, oligonucleotides used for antisense therapy should be modified in such a way that they have high stability and low side effects. This can be done by chemically modifying the oligonucleotides like CpG, anti-gene, small non-coding RNAs, etc.).
The chemical modifications allow the oligonucleotides to enter the nucleus and bind their complementary RNA which is also an RNA of interest. They will not allow RNA to form proteins, or they may destroy the RNA molecule thus downregulating the target gene.
Antisense therapy is more effective than other available therapeutic
modalities because oligonucleotides can easily be modified, they have a high affinity to bind targeted mRNA, they are highly specific, and have no side effects.
Gendicine was the first antisense therapeutic drug that was approved for head and neck cancer in China. This and other drugs available for the treatment of different cancer types usually target the cancer-promoting genes in the cell (Sharad, 2019).
Role of Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy in Cancer
The use of oligonucleotides for the treatment of cancer patients is found to be a very effective therapy. many drugs approved by Food and Drug Regulatory Authority are available in the market and are being used commonly.Antisense therapy is effective in the sense that it can distinguish between the normal and mutated oncogenes in cells and targets only mutated oncogenes without downregulating the expression of normal genes. It can also recognize a single mRNA class in the cell and the specific location of targeted DNA as well.
When oligonucleotide-based drugs are given to the cancer patient, the drugs target the specific mutated genes in cancerous cells. They bind the complementary RNA that will be either degraded in the cell or will not be able to translate into proteins thus affecting the expression of oncogenes in the cell. When these tumor-promoting genes are downregulated in the cell, they will not be able to promote cancer in that cell. Thus, oligonucleotides stop the metastasis and invasion of tumors (Jansen & Zangemeister-Wittke, 2002).
The oligonucleotide sequence binds the mRNA in the cell and prevents the synthesis of specific proteins from it. This prevention may result when oligonucleotides cause inhibition of the translation process, they may prevent the spicing of exons, or they inhibit the transport of mRNA from the nucleus into the cytoplasm which is important for translation to occur.
The oligonucleotides are of specific sequences complementary to the target RNA or DNA sequence. The process is based on finding that a DNA sequence of 17 or more than 17 base pairs is found once in the genome. Similarly, an RNA sequence of 13 base pairs or more is also found only once in the whole genome. So, there is no chance of multiple complementary sites for oligonucleotides in the genome and hence no harm to normal cells. These oligonucleotides must be delivered into the nucleus to the target nucleic acid either DNA or RNA. For this, they have to enter the cell, cross the cytoplasm and move into the nucleus.
The oligonucleotides may cross the cell membrane by the formation of endosomes. This process requires energy. Sometimes the drug can cross the cell membrane without the expenditure of energy if the plasma membrane is permeable for that drug.
In tissue culture techniques, lipophilic molecules are used called liposomes for the effective delivery of drugs into the cell. As most of the drugs are anionic in nature and they cannot cross the plasma membrane.
First we instruct a person from local labs that will draw the blood as well as instructions for how to pack and ship the sample.
We then take the sample of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) from patients blood and categorize the various proteins that are produced by these micro RNAs and classify them to grade the targets as less aggressive to very highly aggressive. Then they will make the treatment to silence the Micro RNA of the given target.
SOT is administered intravenously and takes approximately 90 minutes for the full appointment.
Time frame, the whole process takes 4-5 weeks to be completed.
When an antisense therapeutic drug has entered the cell or nucleus, it causes inhibition of gene expression in the nucleus. This inhibition is usually done at the ribosomal entry site by sterically hindering the RNA molecules in the nucleus. It also brings RNase H into the nucleus. RNase H is found both in the nucleus and the cytoplasm. It cuts the RNA strand in the RNA-DNA hybrid during transcription. And it does not allow the translation of RNA into proteins.
Oligonucleotides only activate the Endo nucleolytic process in the specific RNA molecules by activating RNase H. it will cleave the target RNA molecule, thus decreasing the expression of a specific gene in the cell. As this cleaved RNA will not be translated into the proteins that will affect many activities in the cell.
In cancer cells, many tumor-promoting genes are activated, which will simulate the processes like cell proliferation, division, growth, and metastasis of cancer to other neighboring cells and tissues. The antisense drugs or oligonucleotides are usually given to the patients in naked form, and they target the RNA of these oncogenes or proteins in the nucleus. This will downregulate the expression of these genes. As a result, a very low quantity of proteins is formed or sometimes no proteins are formed in the cell. This loss of function of these proteins will result in the inhibition of all activities like cell proliferation and metastasis. Thus, cancer cells cannot survive anymore.
Current research on antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) in cancer
Many new therapeutic modalities are being introduced to target cancer in the patient’s body. One of the most effective therapies whose use is growing exponentially day by day is the use of antisense oligonucleotides against cancer. It is a promising therapy against cancer and genetic disorders that specifically targets RNA. It inhibits the RNA and thus prevents the synthesis of many important proteins in the cell.
Currently, a drug named AZD8701 is in clinical trials that acts as an antisense inhibitor against the FOXP3 gene, preventing the synthesis of protein and thus activating the immune system against cancer cells (Shang et al., 2022).
Similarly, an antisense inhibitor against heat shock protein 27 (Hsp27) is also in clinical trials for the treatment of prostate cancer patients. Hsp27 is found to be involved in the progression of prostate cancer. So, targeting the RNA of Hsp27 and inhibiting its synthesis will obviously slow down the progression of prostate cancer in patients and this can act as a promising therapy (Le et al., 2022).
Conclusion
The use of oligonucleotides for downregulating the expression of specific genes is an important therapeutic modality against cancer. Many inhibitory drugs are approved by the FDA and have multiple types of cancer. They inhibit protein synthesis by various mechanisms. Some drugs are in clinical trials against many cancers. The use of ASOs can be a promising therapy against cancer.

IMPACT OF HIGH-DOSE INTRAVENOUS VITAMIN C ON CANCERS WITH BRAF & KRAS MUTATIONS
IMPACT OF HIGH-DOSE INTRAVENOUS VITAMIN C ON CANCERS WITH BRAF & KRAS MUTATIONS As soon as someone talks about winter, oranges are the first

Antisense BCL-2 and HER-2 Oligonucleotide Therapy in Breast Cancer
Antisense BCL-2 and HER-2 Oligonucleotide Therapy in Breast Cancer HER2 Positive Breast Cancer Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) is involved in the

Role of Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy in Pancreatic Cancer
Role of Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy in Pancreatic Cancer Antisense oligonucleotides Oligonucleotides are short sequences of nucleic acids either DNA or RNA that can bind

Chemosensitization by Antisense Oligonucleotides Targeting MDM2 Expression
Chemosensitization by Antisense Oligonucleotides Targeting MDM2 Expression MDM2 gene MDM2 oncogene in humans encodes Mouse double minute 2 homolog or MDM2 protein. This protein

Progesterone Antisense Oligonucleotides Inhibits Breast Cancer Growth
Progesterone Antisense Oligonucleotides Inhibits Breast Cancer Growth Hormone status of breast cancer Breast cancer arises from the growth of an abnormal mass of cells

Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy in Oncology
Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy in Oncology Summary Antisense oligonucleotide therapy plays a vital role in cancer and genetic disorders. This therapy involves the use of

A Breakthrough in Cancer Treatment: How Successful is Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs)
A Breakthrough in Cancer Treatment: How Successful is Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs) Oligonucleotides Small sequences of nucleic acids, either DNA or RNA that have many

Chemotherapy With Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy Improves Disease-Free Survival
Chemotherapy With Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy Improves Disease-Free Survival Chemotherapy Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that involves the use of medication to eradicate cancer cells.