H1 Tag: As Title
Introduction: As Meta Description
Form
Precision Oncology & Holistic Approach to Cancer Treatment at Art of Healing Cancer
At Art of Healing Cancer, the fusion of Precision Oncology, modern medicine, and traditional healing practices forms the cornerstone of our patient-centered treatment philosophy. Recognizing the uniqueness of each individual’s battle with cancer, we integrate cutting-edge genomic sequencing and the latest medical advancements to tailor treatment plans that are as unique as the patients themselves. Simultaneously, we embrace the wisdom of traditional medicine, acknowledging its role in nurturing the whole person – body, mind, and spirit. This holistic approach not only targets the cancer cells but also supports the overall well-being of our patients, helping them to maintain a better quality of life throughout their treatment journey. By blending these diverse modalities, Art of Healing Cancer offers a compassionate, comprehensive care plan that addresses the multifaceted challenges of cancer, ensuring that each patient receives the most effective, personalized therapy.
Thyroid cancer Treatment in ____________________________
Please share your contact details for our teams to connect and guide you through your treatment plans
Form
Why Choose Art of Healing Cancer

Blending traditional and modern treatments, we offer a holistic approach to cancer care.
Through chemosensitivity planning, we customize chemotherapy to each patient’s unique needs.
Precision and improved outcomes are hallmarks of our state-of-the-art robotic surgery techniques.
Utilizing genomic and transcriptomic data analysis, we provide the most advanced targeted therapy options.
As the only institution in India combining genomic and transcriptomic data with natural and herbal treatments, we offer comprehensive care.
We offer the most advanced immunotherapy treatments, including tailored vaccines and sensitivity testing to immunotherapy drugs.
One of the only centres trained on exploiting tumor Metabolism
Our Expert Cancer Care Team
At Art of Healing Cancer, we pride ourselves on having a team of highly skilled and compassionate experts in cancer treatment. Our specialists, drawn from diverse fields of oncology, integrate the latest advancements in modern medicine with traditional healing practices. This unique blend ensures that each patient receives a holistic treatment plan, tailored to their specific needs. Our team includes renowned oncologists, experienced surgeons, dedicated nurses, and supportive care professionals who work together to provide comprehensive care.

DR. MANDEEP SINGH MALHOTRA
- Surgical and Molecular Oncologist is the Chief Mentor at Art of Healing Cancer, with over 20 years of clinical oncology experience.
- He is MBBS(MAMC) and MS Surgery (GMC)
- Trained in surgical oncology at All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Delhi, and gained international experience in the UK, USA, and Europe during his Fellowships in Head Neck Oncology; Breast Oncoplasty; Robotic Surgery and Molecular Oncology Certification
- Experienced Robotic Surgeon, he is one of the pioneers for Robot Assisted Functional Breast Preservation.
- Molecular Oncology Certification from RGCC College Europe
- Expert in Advanced and Recurrent Cancer Treatment, utilizing Precision Oncology Techniques such as NGS, Transcriptomics, Tumor Vialbility assays and mapping them to plan Chemotherapy, Immunotherapy and Traditional / Off label medicine & Metabolic Therapy

DR. MOHIT SAXENA
- Senior Consultant in Medical Oncology with over 10 years of experience at Marengo Asia Hospitals, Gurugram.
- Holds MBBS and MD degrees from Sawai Man Singh Medical College, Jaipur; specialized in Medical Oncology from Gujarat Cancer & Research Institute, Ahmedabad.
- Expert in immunotherapy, various chemotherapy techniques (intravenous, intrathecal, oral), targeted therapy, precision medicine, and hormone therapy.
- Skilled in treating cancers of the head & neck, breast, lung, GI tract, hepatobiliary system, and genitourinary organs.
- Published multiple papers in respected national and international journals on cancer research.
- Previous roles include Artemis Hospital and C.K. Birla Hospital, highlighting extensive clinical experience.
- Known for research in hematological malignancies and advanced cancer treatment methods.

DR. SIDDHARTH SAHAI
- He is a medical Oncologist with 11+ years of experience.
- Siddharth has done MBBS from Maulana Azad Medical College, MD from Lady Harding Medical College, DM in Medical Oncology from AIIMS, New Delhi.
- Cleared ESMO Certification in 2013; trained in chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and comprehensive oncology care.
- Focuses on solid tumors including head & neck, thoracic, breast, GI tract, hepatic, genitourinary malignancies, sarcomas, and brain tumors.
- Active member of ASCO, ESMO, SOMOI, ISMO.
- Worked at Venkateshwar Hospital, FMRI, Paras Hospital, Manipal Hospital, Max Hospital in New Delhi and Gurugram, India.

DR. RITESH SHARMA
- Dr. Ritesh is a senior Consultant Radiation Oncologist at Batra Hospital, Delhi, Dr. Ritesh Sharma.
- He has been trained at Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute, Delhi, and Max Cancer Center, Saket.
- 13 years of experience in Radiation Oncology.
- Specializes in SRS/SRT for brain tumors, SBRT for lung, liver, and spine, and hypofractionation for various malignancies.
- Proficient in 4D CT for treating moving tumors and brachytherapy for various cancers.
- Education includes MBBS and MD in Radiotherapy from Gandhi Medical College, Bhopal.
- Involved in research with several published papers.
Chemodaycare with a Difference
The AOHC Chemotherapy Daycare is unique for integrating a Hyperbaric Oxygen Chamber with chemotherapy, enhancing patient recovery. It also offers additional treatments like IV Vitamin C, promoting a holistic approach to cancer care.
Personalized Chemotherapy through Chemosensitivity / Tumour Viability
- Culturing Cancer Cells: Isolate and grow cancer stem cells in a lab to replicate the tumor environment.
- Drug Exposure: Introduce chemotherapeutic drugs to the cultured cells to test their effectiveness.
- Inhibition Assessment: Measure the drugs’ ability to inhibit cancer cell growth or induce cell death, guiding treatment choices. The results provide valuable insights into which chemotherapeutic agents are likely to be most effective in treating the specific cancer type, potentially guiding personalized treatment plans for patients.
HBOT
- HBOT mitigates tumor hypoxia, reducing cancer progression and resistance by enhancing tissue oxygenation.
- Increased plasma oxygen through HBOT reaches areas typically inaccessible to red blood cells, diminishing cancer cell advantages.
- HBOT, when paired with chemotherapy, boosts treatment efficacy by elevating ROS levels, especially effective if chemotherapy follows HBOT.
IV VITAMIN C
- Our organization administers high-dose IV Vitamin C at our chemo daycare facility, significantly enhancing serum vitamin C levels to target cancer cells effectively.
- By incorporating IV Vitamin C, we potentiate chemotherapy’s effectiveness, leveraging its ability to increase the cytotoxic impact on tumor cells while aiming to reduce treatment side effects.
- This integrated approach, supported by extensive research, underscores our commitment to providing advanced, comprehensive cancer care at our daycare facility.
Publications
International journal of Complementary and Internal Medicine
Impact of Slow- Infusion (Metronomic) 2-Deoxy-D-Glucose in Treatment of Refractory Patient of Gliobalstoma Multiforme
Cost of Thyroid Cancer Treatment
The cost of thyroid cancer treatment can vary widely based on factors like cancer type and stage, treatments required. Here’s a general breakdown of potential costs:
- Ultrasound: INR 1,000 to INR 3,000
- Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNAB): INR 2,500 to INR 10,000
- Blood tests (including thyroid function tests): INR 500 to INR 2,500
- Advanced imaging (CT/MRI): INR 5,000 to INR 20,000
- Thyroidectomy (Partial or Total): INR 50,000 to INR 2,00,000, depending on the complexity, the surgeon’s fees, and the type of hospital (private or government).
- Neck Dissection (if required): Additional costs from INR 50,000 to INR 1,50,000 may apply.
- A complete course ranges from INR 1,00,000 to INR 2,50,000, based on session type and number.
- Costs per cycle range from INR 20,000 to INR 2,00,000, with total varying by drugs used and cycle number.
- Monthly costs can be INR 50,000 to over INR 1,00,000, depending on medications.
- Often exceeds INR 1,00,000 per dose, potentially spanning several doses.
- Includes side effect management, physical therapy, counseling, alternative therapies, adding significantly to total cost.
- Regular appointments, tests, and monitoring for recurrence are ongoing costs.
Factors Influencing Treatment Costs
Stage of Cancer
Treatment Plan
Personalized Treatment Approaches
Art of Healing Cancer: Pioneering Robotic Thyroid Cancer Surgery
Art of Healing Cancer proudly stands among the first in the nation to offer robotic thyroid cancer surgery. This advanced technique enhances precision, reduces recovery time, and minimizes scarring, representing a significant leap forward in surgical oncology and patient care
The Transoral Vestibular Approach Robotic Thyroidectomy
The TOVA robotic thyroidectomy technique involves accessing the thyroid gland through the oral vestibule, the space between the lips and gums. Utilizing robotic-assisted technology, surgeons meticulously navigate through natural tissue planes to reach the thyroid gland, obviating the need for external neck incisions. This scarless approach not only addresses cosmetic concerns but also minimizes the risk of surgical complications associated with conventional neck surgery, such as injury to the recurrent laryngeal nerve and parathyroid glands.
It maintains excellent preservation of vital structures within the neck, including the recurrent laryngeal nerve and parathyroid glands, thereby reducing the risk of postoperative complications such as voice changes and hypoparathyroidism.

Advantages of Robotic Surgery:
- Enhanced Precision: Robotic systems provide surgeons with unparalleled control and precision, reducing the risk of damage to surrounding tissues.
- Greater Dexterity: Robotic arms can rotate and bend beyond the capabilities of the human hand, allowing for more complex maneuvers.
- Improved Visualization: The 3D HD vision system offers a magnified, high-resolution image of the surgical site.
- Less Invasive: Robotic surgery involves small incisions, leading to less pain and faster recovery.
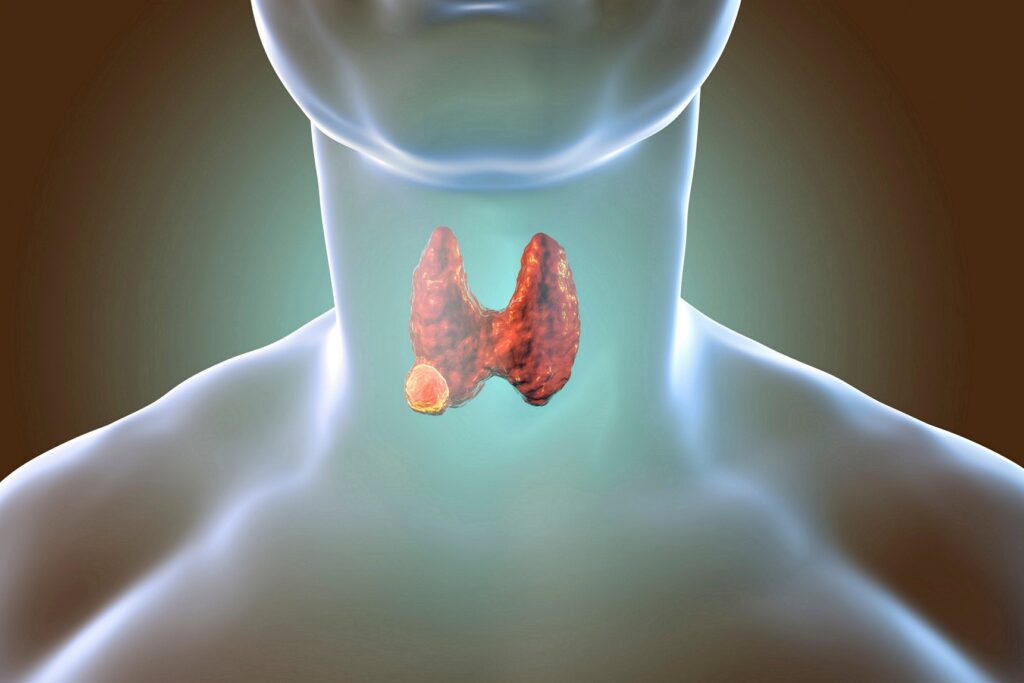
Thyroid Cancer – Introduction & Treatment Methodology
Thyroid cancer starts when cells in the thyroid gland, a small, butterfly-shaped gland at the front of your neck, begin to grow uncontrollably. This growth can form a tumor. Further, these cancer cells can break away from the original tumor and metastasize to other parts of the body, which makes the cancer harder to treat.
This is the most common type. It usually grows slowly and often stays within the thyroid gland. When caught early, it’s typically very treatable. Think of it like a plant that grows slowly in a pot; it doesn’t usually spill over.
This type is less common than papillary and is a bit like a sneaky cousin. It can sometimes spread to other parts of the body, like the lungs or bones, but it’s still treatable, especially if caught early.
This type is rarer and a bit more complex. It can be linked to genetic changes, meaning it might run in families. It’s like a rare plant that requires special attention and care.
This is the rarest and most aggressive type. It grows quickly and is more challenging to treat. Imagine a weed that sprouts fast and is hard to control.
Causes and Risk Factors of Thyroid Cancer
For reasons not entirely clear, thyroid cancer is more common in women and tends to show up more as people get older.
Sometimes, the risk of thyroid cancer is passed down in families, like an unwanted heirloom. Certain genetic conditions can make thyroid cancer more likely.
Being exposed to high levels of radiation is like planting seeds for thyroid cancer, especially if the exposure happens in childhood. This can include medical treatments or environmental exposure.
The thyroid needs iodine, found in table salt and seafood, to work properly. Too little or too much can upset the balance, but the link to cancer is more like a whisper than a shout.
If someone has had thyroid problems in the past, like benign (non-cancerous) thyroid conditions, they might be at a slightly higher risk.
While not as directly linked as in other cancers, overall health and lifestyle choices might play a supporting role in the risk of developing thyroid cancer.
Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer
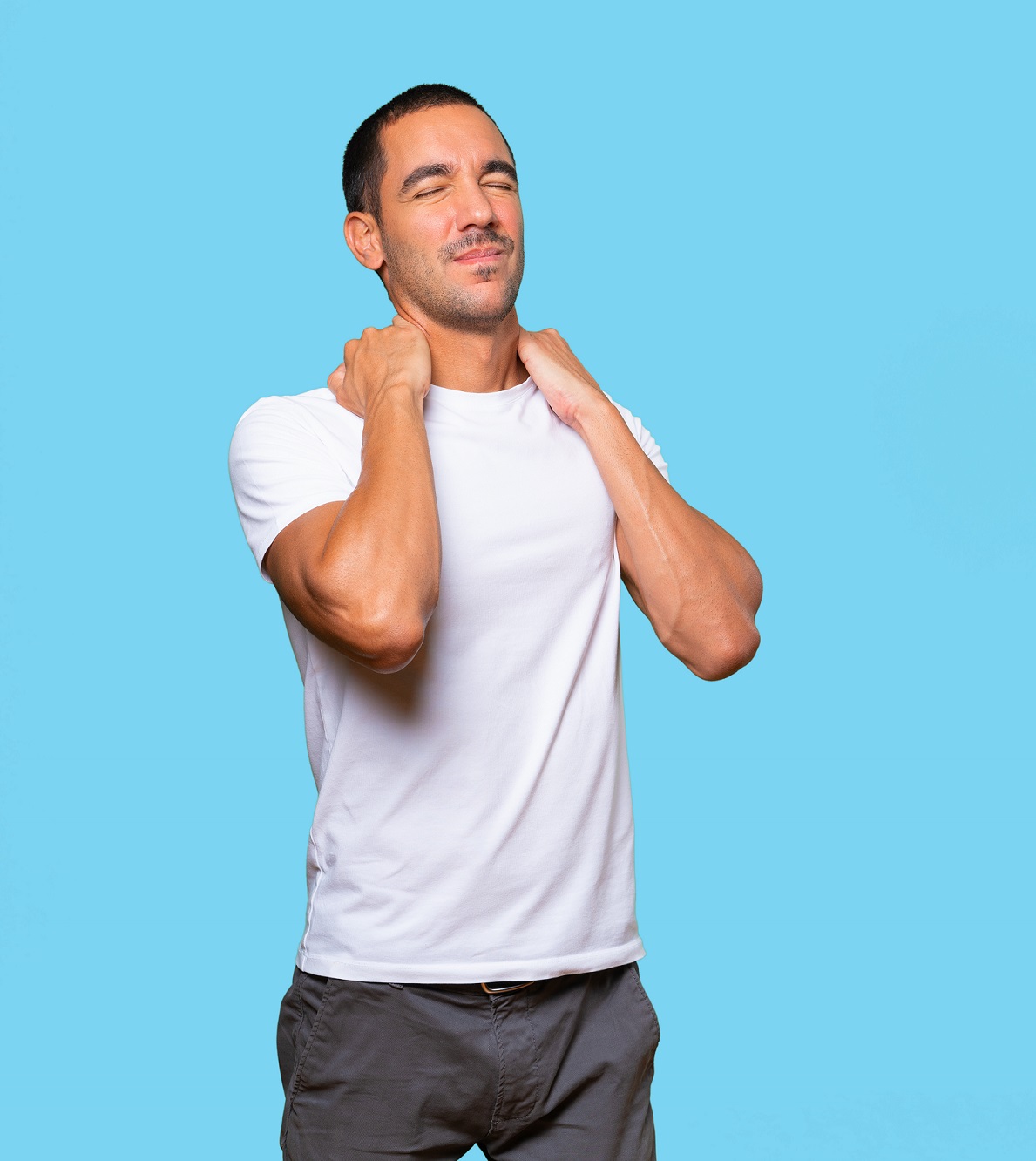

This is the most common sign. A small bump or swelling in the front of your neck, where the thyroid gland sits.
The thyroid is near the vocal cords, so a growing tumor might press on them and make the voice sound hoarse or different.
A larger thyroid tumor might make swallowing feel awkward or uncomfortable, like there’s a hitch in the smooth journey your food usually takes down your throat.
If the tumor grows big enough, it might press on the windpipe, making it difficult to breathe.
The pain might start in the front of the neck and sometimes spread up to the ears. It’s like having an unwelcome tension in the neck that doesn’t easily go away with a simple stretch.
A cough that doesn’t seem to be related to a cold or allergies and doesn’t go away might be a sign of thyroid cancer.
Diagnostic approaches
Doctors start by feeling the neck for any abnormalities in the thyroid, such as lumps (nodules).
This imaging test uses sound waves to create pictures of the thyroid gland and can identify suspicious nodules.
These tests check for abnormal levels of thyroid hormones or thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to assess thyroid function.
A small needle is used to remove cells from a thyroid nodule. These cells are then examined under a microscope to look for cancer.
Tests like CT scans, MRI, or nuclear medicine scans can help determine if the cancer has spread beyond the thyroid.
In some cases, tests are done to look for genetic mutations that might suggest certain types of thyroid cancer.

Stages of Thyroid Cancer
The cancer is small and confined within the thyroid. It’s the earliest stage, offering high treatment success rates.
Cancer might be larger or extend just outside the thyroid but hasn’t spread far. Treatment is still highly effective.
The cancer has grown beyond the thyroid and may involve nearby lymph nodes. Treatment involves a more comprehensive approach.
This advanced stage means the cancer has spread to distant parts of the body. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Treatment Options
- Thyroidectomy: This is the primary surgical treatment for thyroid cancer and involves removing part or all of the thyroid gland.
- Total Thyroidectomy: Removes the entire thyroid gland and is often recommended for larger or more aggressive cancers, or when cancer is found in both lobes of the thyroid.
- Lobectomy: Involves removing one lobe (half) of the thyroid. It’s an option for smaller cancers (<1 cm) confined to one lobe and with no evidence of lymph node involvement.
- Neck Dissection: When thyroid cancer spreads to lymph nodes in the neck, a neck dissection may be performed to remove affected lymph nodes. This helps in staging the cancer and planning further treatment, such as radioactive iodine therapy.
- Central Neck Dissection: Targets lymph nodes in the central compartment of the neck, close to the thyroid gland.
- Lateral Neck Dissection: Involves removing lymph nodes from the side of the neck when cancer has spread more extensively.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: For selected small, low-risk cancers, minimally invasive approaches may be used, leading to smaller incisions, less pain, and quicker recovery.
- Thyroid Lobectomy with Isthmusectomy: Removes one lobe of the thyroid and the isthmus, a small piece of tissue that connects the two lobes. This is an option for cancers that are slightly larger or located in the isthmus.
- Completion Thyroidectomy: Performed if cancer is found in the remaining thyroid tissue after a lobectomy, or if recurrent cancer is detected.
Uses cytotoxic drugs to target rapidly dividing cancer cells, administered intravenously, orally, or by injection. Types include Anthracyclines, Taxanes, Alkylating Agents, and Antimetabolites. Can be neoadjuvant (before surgery), adjuvant (after surgery), or palliative.
Radioactive iodine, specifically iodine-131, emits beta particles that penetrate thyroid cells, causing cellular damage and ultimately leading to their destruction. This process, known as radioiodine ablation, capitalizes on the fact that thyroid cells, including cancerous ones, possess a high affinity for iodine, a crucial component in thyroid hormone synthesis. By administering radioactive iodine orally or intravenously, clinicians can selectively target and eliminate cancerous thyroid tissue while minimizing adverse effects on other organs. RAI therapy is invaluable in treating metastatic thyroid cancer, where cancerous cells have spread to distant sites such as the lungs or bones.
Focuses on specific genes or proteins involved in cancer growth.
- Monoclonal Antibodies: Bind to cancer cell molecules, blocking growth or aiding immune response.
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Block enzymes promoting cancer cell growth.
- Proteasome Inhibitors: Hinder protein breakdown needed for cancer cell survival.
- Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: Affect gene expression regulation in cancer cells.
Enhances the body’s immune response against cancer.
- Checkpoint Inhibitors: Unblock immune cells to attack cancer.
- Monoclonal Antibodies: Target specific cancer cells.
- Cancer Vaccines: Train the immune system to recognize cancer cells.
- Adoptive Cell Therapy: Modifies patient’s immune cells to better fight cancer.
- Oncolytic Virus Therapy: Uses viruses to target and destroy cancer cells.
Uses high-energy beams to kill or halt cancer cell growth.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): Directs radiation from outside the body.
- Internal Radiation Therapy (Brachytherapy): Places radioactive material near cancer cells.
- Systemic Radiation Therapy: Uses radioactive substances in the blood.
- Proton Therapy: Utilizes protons for precise targeting.
Customizes treatment based on genetic profiling of cancer.
- Genomic Sequencing (NGS): Identifies specific mutations for targeted therapies.
- Chemosensitivity: Tests cancer cell response to chemotherapy drugs.
- RNA Sequencing: Analyzes gene expression for targeted interventions.
- Tissue Banking: Stores samples for future research.
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC): Monitors disease progression through blood analysis.
- Metabolic Therapy: Targets cancer cell metabolism through dietary changes.
Integrative Cancer Treatments at Art of Healing Cancer

Administering high-dose Vitamin C intravenously, this therapy is explored for its potential to produce hydrogen peroxide, which may target cancer cells, enhance life quality, and mitigate side effects of traditional treatments.
An innovative therapy where patients inhale molecular hydrogen gas, leveraging its antioxidant properties to potentially reduce oxidative stress in cancer cells. Its efficacy and safety in humans are subjects of ongoing research.
Involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized environment, believed to enhance tissue oxygenation and aid healing. Used cautiously in cancer care to potentially improve chemotherapy and radiation effectiveness and manage side effects.
Utilizes extracts from the European mistletoe plant, injected to possibly stimulate the immune system and exert cytotoxic effects on cancer cells. While popular in Europe for quality of life improvement, its scientific validation remains mixed.
An ancient Indian practice focusing on body system balance through diet, herbal treatment, and yogic breathing. Aimed at detoxification, boosting defense mechanisms, and overall well-being, it complements conventional treatments despite limited clinical trial evidence.
Targeted therapies, like tyrosine kinase inhibitors, have revolutionized the treatment landscape for lung cancer. These therapies specifically target molecular changes seen in cancer cells. For example, drugs like gefitinib, erlotinib, and afatinib have been successful against specific types of NSCLC.
Immunotherapy has emerged as a game-changer, especially for advanced lung cancer. It includes checkpoint inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies, and adoptive cell therapies. Drugs like nivolumab and pembrolizumab have shown remarkable results in treating NSCLC by reactivating the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
Radiation therapy has evolved significantly, with techniques like 3D-CRT, IMRT, SRS, and SBRT offering more precision and minimizing damage to healthy tissues. Advances like IGRT and ART allow for real-time adjustments, enhancing treatment accuracy and outcomes.
Precision oncology represents a paradigm shift in cancer treatment, with Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) enabling a comprehensive genomic analysis. This approach allows for the development of personalized treatment plans, targeting specific genetic mutations and alterations in cancer cells.
Chemosensitivity testing evaluates how cancer cells respond to different chemotherapy drugs, reducing the trial-and-error approach in selecting effective treatments. This predictive analysis can significantly enhance treatment efficacy.
Metabolic therapy targets the unique metabolic requirements of cancer cells, disrupting their growth and survival pathways. Dietary interventions play a role in this approach, complementing conventional treatments.
Metabolic therapy targets the unique metabolic requirements of cancer cells, disrupting their growth and survival pathways. Dietary interventions play a role in this approach, complementing conventional treatments.
Stress reduction and emotional well-being are critical components of lung cancer care. Practices like meditation, yoga, and tai chi offer significant benefits in stress management and physical recovery.
