test liver cancer
meta desc
heading 2
content 2
heading 3
content 3
Why Choose Art of Healing Cancer

Blending traditional and modern treatments, we offer a holistic approach to cancer care.
Through chemosensitivity planning, we customize chemotherapy to each patient’s unique needs.
Precision and improved outcomes are hallmarks of our state-of-the-art robotic surgery techniques.
Utilizing genomic and transcriptomic data analysis, we provide the most advanced targeted therapy options.
As the only institution in India combining genomic and transcriptomic data with natural and herbal treatments, we offer comprehensive care.
We offer the most advanced immunotherapy treatments, including tailored vaccines and sensitivity testing to immunotherapy drugs.
One of the only centres trained on exploiting tumor Metabolism
heading 4
content 4

DR. MANDEEP SINGH MALHOTRA
- Surgical and Molecular Oncologist is the Chief Mentor at Art of Healing Cancer, with over 20 years of clinical oncology experience.
- He is MBBS(MAMC) and MS Surgery (GMC)
- Trained in surgical oncology at All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Delhi, and gained international experience in the UK, USA, and Europe during his Fellowships in Head Neck Oncology; Breast Oncoplasty; Robotic Surgery and Molecular Oncology Certification
- Experienced Robotic Surgeon, he is one of the pioneers for Robot Assisted Functional Breast Preservation.
- Molecular Oncology Certification from RGCC College Europe
- Expert in Advanced and Recurrent Cancer Treatment, utilizing Precision Oncology Techniques such as NGS, Transcriptomics, Tumor Vialbility assays and mapping them to plan Chemotherapy, Immunotherapy and Traditional / Off label medicine & Metabolic Therapy

DR. MOHIT SAXENA
- Senior Consultant in Medical Oncology with over 10 years of experience at Marengo Asia Hospitals, Gurugram.
- Holds MBBS and MD degrees from Sawai Man Singh Medical College, Jaipur; specialized in Medical Oncology from Gujarat Cancer & Research Institute, Ahmedabad.
- Expert in immunotherapy, various chemotherapy techniques (intravenous, intrathecal, oral), targeted therapy, precision medicine, and hormone therapy.
- Skilled in treating cancers of the head & neck, breast, lung, GI tract, hepatobiliary system, and genitourinary organs.
- Published multiple papers in respected national and international journals on cancer research.
- Previous roles include Artemis Hospital and C.K. Birla Hospital, highlighting extensive clinical experience.
- Known for research in hematological malignancies and advanced cancer treatment methods.

DR. SIDDHARTH SAHAI
- He is a medical Oncologist with 11+ years of experience.
- Siddharth has done MBBS from Maulana Azad Medical College, MD from Lady Harding Medical College, DM in Medical Oncology from AIIMS, New Delhi.
- Cleared ESMO Certification in 2013; trained in chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and comprehensive oncology care.
- Focuses on solid tumors including head & neck, thoracic, breast, GI tract, hepatic, genitourinary malignancies, sarcomas, and brain tumors.
- Active member of ASCO, ESMO, SOMOI, ISMO.
- Worked at Venkateshwar Hospital, FMRI, Paras Hospital, Manipal Hospital, Max Hospital in New Delhi and Gurugram, India.

DR. RITESH SHARMA
- Dr. Ritesh is a senior Consultant Radiation Oncologist at Batra Hospital, Delhi, Dr. Ritesh Sharma.
- He has been trained at Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute, Delhi, and Max Cancer Center, Saket.
- 13 years of experience in Radiation Oncology.
- Specializes in SRS/SRT for brain tumors, SBRT for lung, liver, and spine, and hypofractionation for various malignancies.
- Proficient in 4D CT for treating moving tumors and brachytherapy for various cancers.
- Education includes MBBS and MD in Radiotherapy from Gandhi Medical College, Bhopal.
- Involved in research with several published papers.
head 5
The AOHC Chemotherapy Daycare is unique for integrating a Hyperbaric Oxygen Chamber with chemotherapy, enhancing patient recovery. It also offers additional treatments like IV Vitamin C, promoting a holistic approach to cancer care.
Personalized Chemotherapy through Chemosensitivity / Tumour Viability
- Culturing Cancer Cells: Isolate and grow cancer stem cells in a lab to replicate the tumor environment.
- Drug Exposure: Introduce chemotherapeutic drugs to the cultured cells to test their effectiveness.
- Inhibition Assessment: Measure the drugs’ ability to inhibit cancer cell growth or induce cell death, guiding treatment choices. The results provide valuable insights into which chemotherapeutic agents are likely to be most effective in treating the specific cancer type, potentially guiding personalized treatment plans for patients.
HBOT
- HBOT mitigates tumor hypoxia, reducing cancer progression and resistance by enhancing tissue oxygenation.
- Increased plasma oxygen through HBOT reaches areas typically inaccessible to red blood cells, diminishing cancer cell advantages.
- HBOT, when paired with chemotherapy, boosts treatment efficacy by elevating ROS levels, especially effective if chemotherapy follows HBOT.
IV VITAMIN C
- Our organization administers high-dose IV Vitamin C at our chemo daycare facility, significantly enhancing serum vitamin C levels to target cancer cells effectively.
- By incorporating IV Vitamin C, we potentiate chemotherapy’s effectiveness, leveraging its ability to increase the cytotoxic impact on tumor cells while aiming to reduce treatment side effects.
- This integrated approach, supported by extensive research, underscores our commitment to providing advanced, comprehensive cancer care at our daycare facility.
Publications
International journal of Complementary and Internal Medicine
Impact of Slow- Infusion (Metronomic) 2-Deoxy-D-Glucose in Treatment of Refractory Patient of Gliobalstoma Multiforme
Cost of Liver Cancer Treatment
The cost of liver cancer treatment can vary widely based on factors like cancer type and stage, treatments required, healthcare facility, and the choice between private or public healthcare services.
- Initial consultation with an oncologist can range from INR 1,000 to INR 3,000.
- Diagnostic tests, including blood tests, ultrasound, CT scans, and MRIs, can range from INR 5,000 to INR 30,000, depending on the tests required.
- A partial hepatectomy (removal of part of the liver) can cost between INR 2,50,000 and INR 5,00,000.
- A liver transplant is significantly more expensive, ranging from INR 20,00,000 to INR 40,00,000, including pre-surgery evaluation, the surgery itself, and post-operative care.
- A complete course ranges from INR 1,00,000 to INR 2,50,000, based on session type and number.
- Costs per cycle range from INR 20,000 to INR 2,00,000, with total varying by drugs used and cycle number.
- Monthly costs can be INR 50,000 to over INR 1,00,000, depending on medications.
- Often exceeds INR 1,00,000 per dose, potentially spanning several doses.
- Includes side effect management, physical therapy, counseling, alternative therapies, adding significantly to total cost.
- Regular appointments, tests, and monitoring for recurrence are ongoing costs.
Factors Influencing Treatment Costs
Stage of Cancer
Treatment Plan
Personalized Treatment Approaches
head 6
Art of Healing Cancer proudly stands among the first in the nation to offer robotic liver cancer surgery. This advanced technique enhances precision, reduces recovery time, and minimizes scarring, representing a significant leap forward in surgical oncology and patient care.

head 7
Liver cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the cells of your liver, a key organ situated in the upper right part of your abdomen, beneath your diaphragm and above your stomach. The liver has several important functions, including detoxifying harmful substances, metabolizing drugs, making proteins that help your blood clot, and producing bile, a substance that aids in digestion.
The most prevalent type, HCC starts in hepatocytes, often due to hepatitis, alcohol use, or fatty liver disease.
This cancer develops in the liver’s bile ducts and is known for its diagnostic and treatment challenges.
Rare and mostly affecting children under 3, hepatoblastoma has a good prognosis when detected early.
A rare HCC variant without underlying liver disease, affecting adolescents and young adults, with a relatively better outlook.
Fast-growing and rare, these start in the liver’s blood vessels, often diagnosed late with a poor prognosis.
Refers to cancer that has spread to the liver from another body part, more common than primary liver cancers.
Testing and Screening for Liver Cancer
Liver function tests check enzymes and proteins in your blood, indicating liver health. High levels of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) may suggest liver cancer, though not exclusively.
Essential for visualizing the liver, these tests identify and assess tumors.
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves for initial liver imaging.
- CT Scan: Offers detailed cross-sectional body images, enhancing liver and organ analysis.
- MRI: Provides high-detail images using magnetic fields, ideal for examining liver tumors and blood vessels.
The removal and microscopic examination of liver tissue to confirm cancer presence and type. Methods include percutaneous (needle through the skin) and surgical biopsies.
A minimally invasive procedure using a laparoscope to view the liver directly, allowing for real-time assessment and biopsy.
Conducted to detect cancer spread to bones, if suspected.
Causes and Risk Factors of Liver Cancer

Long-term hepatitis B and C infections can damage liver cells, significantly raising the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Liver scarring from diseases like alcohol abuse and fatty liver impairs
Excessive, long-term drinking can damage the liver, leading to cirrhosis and heightened liver cancer risk.
Associated with obesity and diabetes, NAFLD involves fat accumulation in the liver, increasing cirrhosis and cancer risk.
Toxins from mold on stored crops can cause liver cancer, particularly where food storage is poorly regulated.
Conditions like hemochromatosis and Wilson’s disease that cause chronic liver damage also elevate liver cancer risk.
High body weight is linked to fatty liver disease and an increased liver cancer risk.
Diabetics, especially those with other risk factors like obesity or hepatitis, are more prone to liver cancer.
Smoking, compounded by other risk factors such as hepatitis, raises the likelihood of liver cancer.
Symptoms of Liver Cancer
Unintentional and unexplained weight loss is a common symptom in many types of cancer, including liver cancer, as the body’s metabolism changes in response to the cancer cells.
People with liver cancer may feel less hungry than usual, leading to a decrease in food intake and weight loss.
Pain or discomfort in the upper right side of the abdomen can occur as the liver enlarges or due to a tumor pressing on surrounding tissues.
Liver cancer can cause a feeling of fullness after only a small amount of food, often because the enlarged liver presses on the stomach.
These symptoms can arise from the pressure of the enlarged liver on the stomach or from the general effects of cancer on the body.
Ongoing tiredness that doesn’t improve with rest can be a sign of liver cancer, as the body diverts energy to fight the cancer.
This is the yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes caused by the buildup of bilirubin, a substance produced by the liver. It can indicate that the liver is not functioning properly due to cancer.
Fluid buildup, known as ascites, can cause swelling in the abdomen. This may be due to the liver’s reduced ability to produce proteins that regulate fluid balances.
Accumulation of bile products in the body can lead to persistent itching.
If cancer blocks the bile ducts, bile cannot reach the intestines, and the stool may become pale or chalky white.

Stages of Liver Cancer
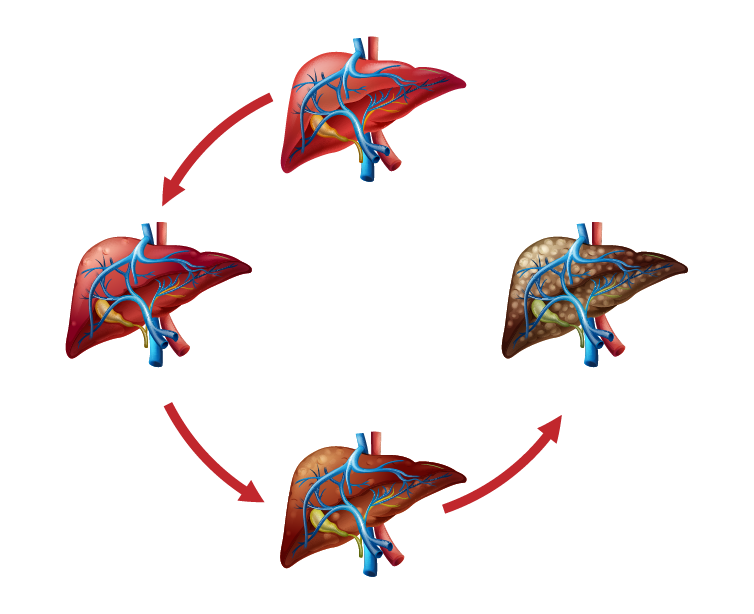
A single tumor exists without blood vessel invasion, confined solely to the liver, presenting the best prognosis.
Features either multiple tumors or a single tumor involving a blood vessel, yet remains within the liver without external spread.
Subdivided into:
- Stage IIIA: Multiple tumors present, with at least one exceeding 5 cm, yet no spread to lymph nodes or distant locations.
- Stage IIIB: Cancer extends to nearby structures like the gallbladder but not to distant sites or lymph nodes.
- Stage IIIC: Involvement with major liver blood vessels, without reaching lymph nodes or distant areas.
Cancer has metastasized beyond the liver:
- Stage IVA: Spread includes nearby lymph nodes but not distant organs.
- Stage IVB: Cancer has reached distant organs, irrespective of primary tumor characteristics or local extensions.
head 8
Administering high-dose Vitamin C intravenously, this therapy is explored for its potential to produce hydrogen peroxide, which may target cancer cells, enhance life quality, and mitigate side effects of traditional treatments.
An innovative therapy where patients inhale molecular hydrogen gas, leveraging its antioxidant properties to potentially reduce oxidative stress in cancer cells. Its efficacy and safety in humans are subjects of ongoing research.
Involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized environment, believed to enhance tissue oxygenation and aid healing. Used cautiously in cancer care to potentially improve chemotherapy and radiation effectiveness and manage side effects.
Utilizes extracts from the European mistletoe plant, injected to possibly stimulate the immune system and exert cytotoxic effects on cancer cells. While popular in Europe for quality of life improvement, its scientific validation remains mixed.
An ancient Indian practice focusing on body system balance through diet, herbal treatment, and yogic breathing. Aimed at detoxification, boosting defense mechanisms, and overall well-being, it complements conventional treatments despite limited clinical trial evidence.

Treatment Options for Liver Cancer

- Partial Hepatectomy: Removes the cancerous portion of the liver, suitable for those with limited tumors and enough healthy liver, leveraging the liver’s ability to regenerate.
- Liver Transplant: Replaces the entire liver with a healthy donor organ, reserved for early-stage liver cancer patients who can’t undergo hepatectomy due to other liver issues, subject to strict eligibility due to donor organ scarcity.
- Ablation Therapy: Destroys tumors without physical removal. Includes methods like radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for heating and cryoablation for freezing tumors, ideal for smaller tumors or patients unable to have surgery.
- Tumor Embolization: Blocks the tumor’s blood supply to starve it. Variants include transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) with localized chemotherapy and radioembolization for direct radiation, used when surgery isn’t an option.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive approach using small incisions and specialized tools for tumor removal, offering quicker recovery and reduced complications compared to traditional surgery.
Uses cytotoxic drugs to target rapidly dividing cancer cells, administered intravenously, orally, or by injection. Types include Anthracyclines, Taxanes, Alkylating Agents, and Antimetabolites. Can be neoadjuvant (before surgery), adjuvant (after surgery), or palliative.
Focuses on specific genes or proteins involved in cancer growth.
- Monoclonal Antibodies: Bind to cancer cell molecules, blocking growth or aiding immune response.
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Block enzymes promoting cancer cell growth.
- Proteasome Inhibitors: Hinder protein breakdown needed for cancer cell survival.
- Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: Affect gene expression regulation in cancer cells.
Enhances the body’s immune response against cancer.
- Checkpoint Inhibitors: Unblock immune cells to attack cancer.
- Monoclonal Antibodies: Target specific cancer cells.
- Cancer Vaccines: Train the immune system to recognize cancer cells.
- Adoptive Cell Therapy: Modifies patient’s immune cells to better fight cancer.
- Oncolytic Virus Therapy: Uses viruses to target and destroy cancer cells.
Uses high-energy beams to kill or halt cancer cell growth.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): Directs radiation from outside the body.
- Internal Radiation Therapy (Brachytherapy): Places radioactive material near cancer cells.
- Systemic Radiation Therapy: Uses radioactive substances in the blood.
- Proton Therapy: Utilizes protons for precise targeting.
Customizes treatment based on genetic profiling of cancer.
- Genomic Sequencing (NGS): Identifies specific mutations for targeted therapies.
- Chemosensitivity: Tests cancer cell response to chemotherapy drugs.
- RNA Sequencing: Analyzes gene expression for targeted interventions.
- Tissue Banking: Stores samples for future research.
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC): Monitors disease progression through blood analysis.
- Metabolic Therapy: Targets cancer cell metabolism through dietary changes.
Complementary approaches focusing on well-being and symptom management.
- Diet and Nutrition: Emphasizes whole foods and anti-inflammatory items.
- Herbal Supplements: Includes evidence-based herbs for cancer care or symptom relief.
- Mind-Body Therapies: Practices like meditation, yoga, and tai chi for stress reduction.
- IV Vitamin C: High-dose therapy with potential benefits but not widely accepted.
- Hydrogen Inhalation Therapy: Emerging approach with antioxidant properties.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT): Enhances chemotherapy and radiation efficacy, with cautious use.
- Mistletoe Therapy: Used for immune stimulation and quality of life improvement.
- Ayurvedic Medicine: Focuses on holistic care, often alongside conventional treatments.
Each treatment option is chosen based on individual patient factors, cancer stage, and overall health, offering a comprehensive approach to liver cancer management.

