Cancer Prevention
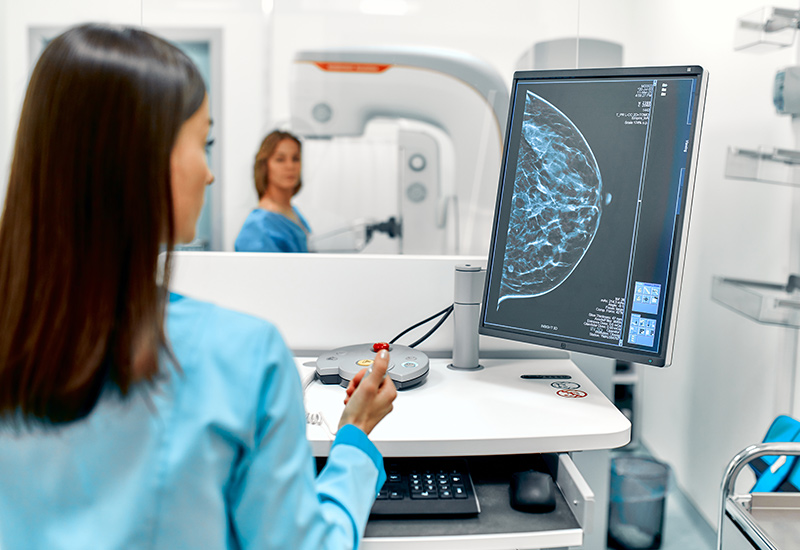
Screening for Breast Cancer
Breast cancer screening helps in the early detection of breast cancer at an early stage. Mammography is the best tool doctors have to screen healthy women for the risk of breast cancer, it is an x-ray of the breast. Mammograms can detect the tumors that are too small and can be felt by the doctor. It’s recommended for the women at average risk of developing breast cancer for screening tests, such as Clinical Breast Exam every one to three years for the age 25 to 39 and mammogram along with the clinical breast exam every year for age 40 and older. When cancer is found early, there are higher chances of successful treatment of the disease. Other ways to examine the breast, such as an Ultrasound or a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan, are not regularly used to screen for breast cancer in women at average risk.
Screening for Cervical Cancer
The screening of Cervical Cancer can help to find cervical cancer in its initial stage. The Pap Test & the HPV test can help prevent cervical cancer or find it early. The Pap test or (Pap smear) looks for precancer cells on the cervix, that might become cervical cancer if not treated appropriately. The HPV test looks for the ‘Human Papilloma Virus’ that can cause these cell changes. The screening for cervical cancer is recommended for women at average risks, such as the Pap test every three years for the age 21 to 29 and the HPV Test & Pap test for the women aged between 30 to 64. Above age 65 or older, women do not need screening exams any longer, if they had no unusual HPV or Pap test results in the past 10 years. Along with the regular exam, awareness is also important by noticing changes like irregular bleeding or discharge.
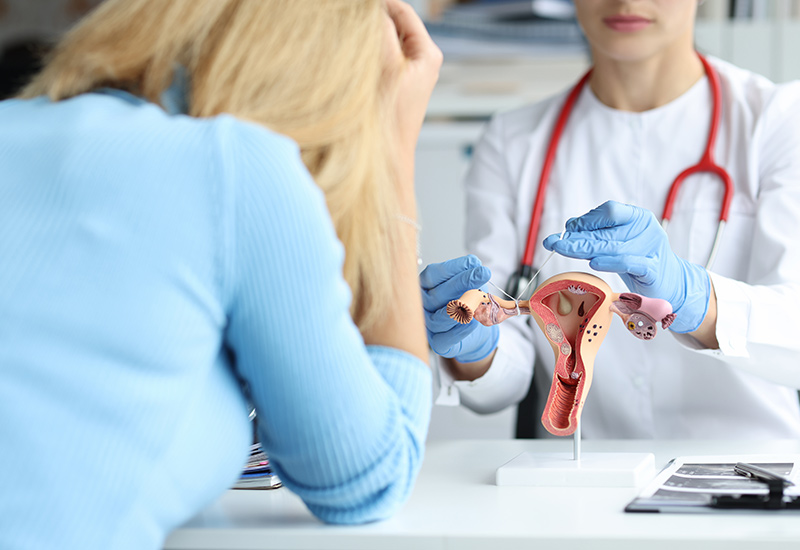
Screening for Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer screening can help decrease the risk of developing ovarian cancer. The mutations that can increase the risk of ovarian cancer can be BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations, Suspected risk of BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations, a close relative who has suspected with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations, Lynch syndrome (Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer). Regular screening is recommended for women, if suspected for any of the mutation, such as Transvaginal ultrasound & CA 125 blood test every 6-12 months. A Salpingo-oophorectomy, or surgery to remove fallopian tubes and ovaries, is strongly recommended for women with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations who are finished having children. Along with regular exams, you should also notice the changes in your body such as abdominal discomfort or pain.
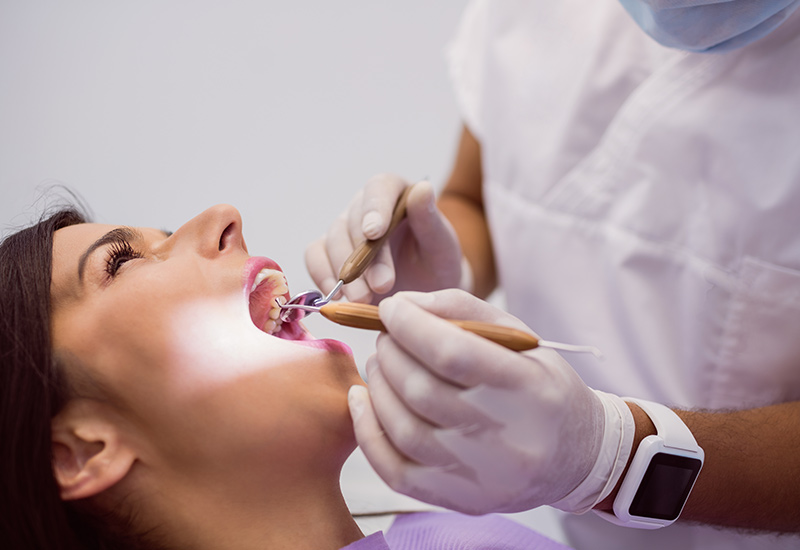
Screening for Oral Cancer
Screening for Oral Cancer helps in identifying mouth cancer in an early stage. Most dentists examine the mouth during a routine dental visit to screen for oral cancer, some dentists may use additional tests to aid in identifying areas of abnormal cells in the mouth, they might also examine the throat & neck for lumps. The screening helps to detect the precancerous condition in the mouth when cancer or lesion are easiest to remove & cure the disease. An increasing number of these cancers are associated with the sexually transmitted infection of human papillomavirus (HPV). Some additional tests for oral cancer screening are ‘Oral Cancer Screening Dye’ and ‘Oral Cancer Screening Light’.